Contribution of Robots to Industrial Automation
Industrial automation came into the limelight in the 1970s when a team of engineers at Honeywell developed the first original distributed control system (DCS). The development of DCS marked the beginning of a long process that has culminated in the production of robots that can work amongst humans.
After engineers at Honeywell developed DCS, an American mechanical engineer known as Dick Morley created the first programmable logic controller (PLC). After that, several innovators released human interface software that would help robots work in a wide range of industries.
If you look at the history of robots, you will realize that some industrial players have been in growth plateaus while others continue to flourish. Some industries have embraced automation better than others. Automation is a continuous process that keeps evolving. New displays, amplifiers, sensors, valves, recorders, actuators, and controls are released every other day.
Understanding Automation in Industries
Industrial automation uses control systems to operate equipment such as machinery and networks. An automated system can complete tasks with minimal or no human intervention.
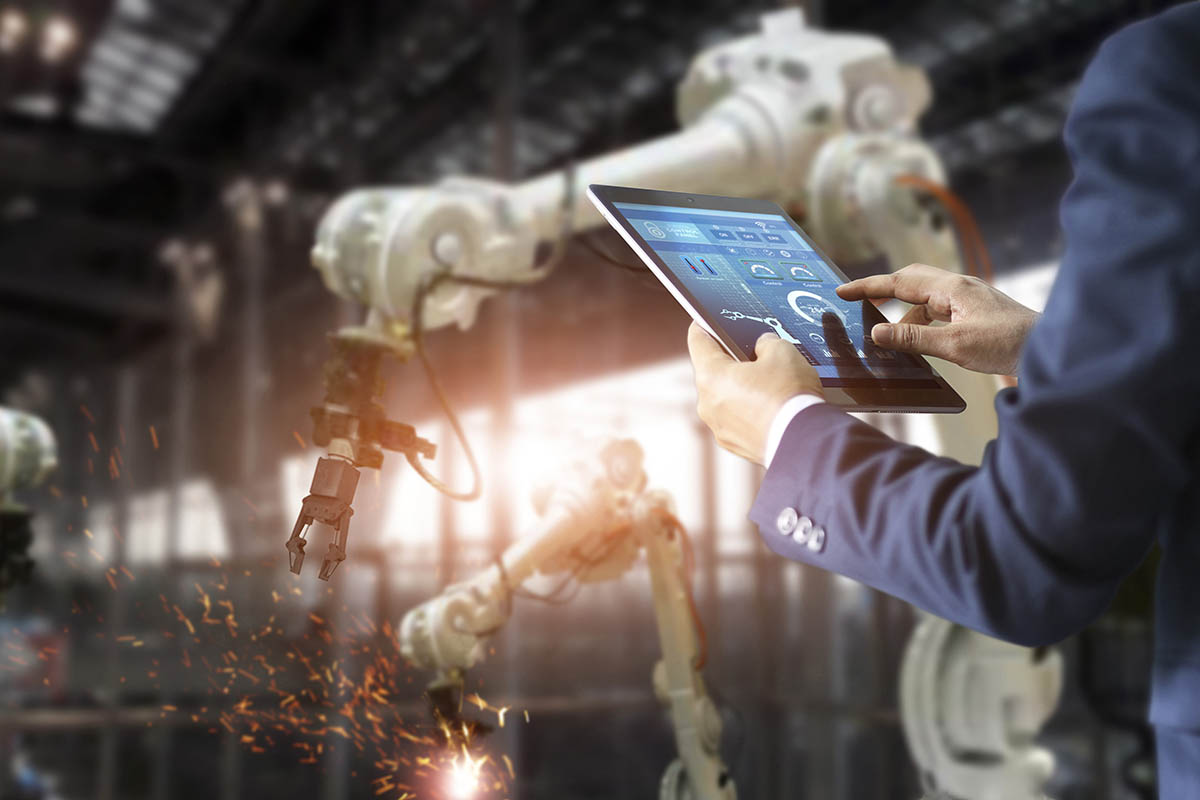
The automotive industry was among the first to adopt the use of robots. General Motors was the first company to establish an automation department. Robots and intelligent machines are used in industries to complete tasks that need stamina, speed, and a high degree of accuracy. Industrial automation benefits a company in many ways.
Industrial automation cannot be complete without hydraulic, mechanical, and electronic systems. Cameras like a GPU Direct Camera also play a role in automation, as they help monitor what is going on and can inform decisions made by other systems or humans monitoring the cameras.
The automation trend hasn’t left behind small and medium-sized manufacturers. Universal robot manufacturers provide automated systems for both large and small manufacturers to help them boost production, increase efficiency, and cut production costs.
How Industrial Automation Has Evolved
The face and functionality of industrial robots have tremendously changed over the years. Robots manufactured in the early 70s were scary and challenging to operate. They occupied large spaces and required special handling. It would take weeks or even months to set up a robot on the production floor.
As the years went by, manufacturers began developing robots that were more flexible and safer. Modern robots are multi-functional, and a single robot can be used to complete different tasks in a factory. For instance, an advanced universal robot can make decisions and work autonomously without human intervention.
Other robots can work safely in confined spaces alongside human workers without the risk of harming human operators. Many manufacturers are choosing to incorporate industrial robots in their production processes for the following reasons.
They have Low Maintenance
We all know that downtime kills a company’s productivity. Sometimes, it can take days or even weeks to service production machines. The time spent maintaining devices interferes with a company’s production. Manufacturers are, therefore, pressuring engineers to develop robots that require less maintenance. Besides, the new robots should be easy to install, operate and maintain.
They are safer
Human safety is a primary concern, especially in industries with robots. However concerns about human safety are a thing of the past as most of the modern robots are designed to collaborate and work amongst humans. Mobile cobots have inbuilt features such as cameras and sensors that sense and predict human behavior. These features go a long way in ensuring the workplace environment is safe.
They are Highly Connected
The industrial revolution focuses on machine learning, interconnectivity, automation, and real-time data collection. Modern industrial robots are designed to collaborate with human operators and other machines. Robots can collect real-time data and send it to a computer for analysis. They can also review production performance to determine underperforming systems.
They are More Intelligent
Artificial intelligence and machine learning make modern robots smarter than their traditional cousins. They can sense and even predict human behavior. They can also complete complicated tasks without human help.