Specimen Collection: Principles and Procedure
Specimen collection refers to obtaining tissue or fluids from patients for laboratory testing. It’s usually the first step towards determining a diagnosis and establishing the right course of treatment. The procedures used must, by all means, minimize the risk of introducing contamination.
The priority is to protect the health and safety of everyone involved in handling the specimen. This is mostly applicable to the patient and staff handling the specimen. It’s also essential that a patient is adequately prepared for the process of specimen collection. Accurate test results also depend on the process of collection and how the specimen is collected.
Importance of Specimen Collection
Specimen collection is a crucial part of the entire process of having a holistic assessment. The specimen collected help in
- Building a clinical representation of the patient
- Making a confirmation of a diagnosis
- Informing a treatment plan
For specimens to help healthcare givers meet the above objectives, a few conditions must be met. The samples must be collected at the right time, the right technique must be applied, and testing must be done soonest possible.
Safety and Disposal Considerations
Healthcare personnel must follow the currently recommended techniques to ensure they maintain sterile conditions in the process. They also must take the necessary precautions in the use and disposal of needles and other equipment.
All biological material and Specimen Collector should be treated as potentially hazardous. The responsibility to adhere to the recommendations for safety for both patients and healthcare workers is long-term. It doesn’t end when a patient is discharged or dismissed from the hospital.
Steps in Obtaining Quality Specimen
Generally, there are four significant steps in collecting specimens for testing.
Preparation
The first step is preparation for the entire process. The most crucial step is to prepare the patient by providing them with adequate instructions on the collection. This includes medication restrictions, diet, and fasting, depending on the specific test to be done.
The specimen must also be prepared by verifying the patient’s identification, which is crucial. All primary specimen collectors must be carefully labeled. The principles of labeling require that at least two identifiers be used at the time of collection.
Examples of identifiers include the patient’s name, date of birth, unique random number, or test request form number. All containers to hold specimens must be labeled in the presence of the patient.
Common problems related to specimen collection can be avoided by giving careful attention to routine procedures. The quality of the specimen must be maintained by using only the materials provided by the laboratory. A sufficient quantity of each sample must also be collected for the procedures to be performed.
Patient’s Consent
Part of preparing a patient for specimen collection is to have their consent to the procedure. To obtain consent from a patient, the healthcare giver must inform the patient why the specimen is being collected. The procedure must carefully be explained, and the patient’s understanding assessed.
The patient also has a right to be informed of how long the test will take and when the results will be ready. It’s also essential to notify them of the implications of care.
Collection
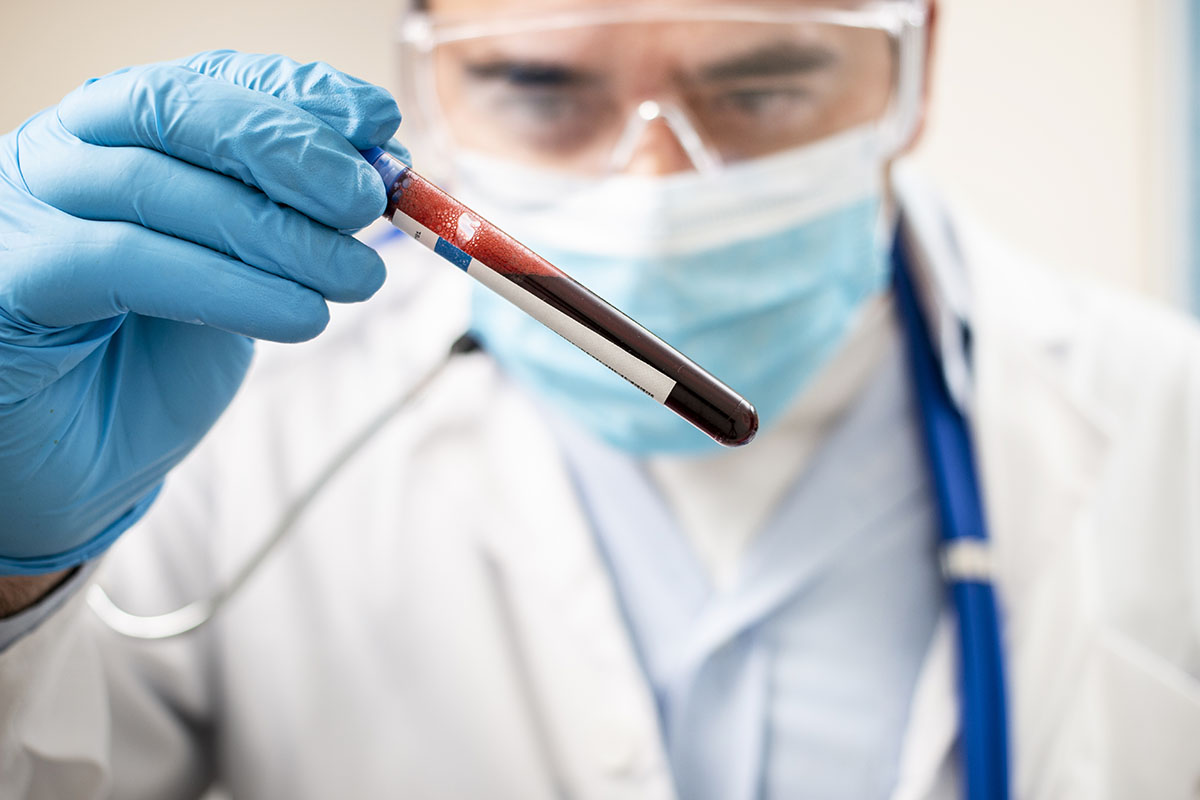
The specimen collected should be enclosed in a secure container and labeled appropriately. Only a waterproof pen should be used to label the container and placed in a waterproof bag. The specimen is collected in blood, vomitus, serum, urine, skin lesions, and mucus. Each type of specimen is collected for a particular kind of test. For example, a fecal specimen is mostly used to establish bacteria, viruses, or parasites in the patient’s body.
Blood is used in the investigation of many conditions. Most commonly, it’s used to detect the presence of antibodies developed as a result of an infection. Blood collection should only be done by legally qualified personnel. Skin lesions like boils, secretions, abscesses, and lesions are typical samples collected from food handlers.
The other steps entail processing the specimen and transporting or storing it appropriately in a freeze dryer or lyophilizers from somewhere like SciQuip (https://www.sciquip.co.uk/
Best Practices for Specimen Collection
Specimen collectors must ensure the samples collected are appropriate to the patient’s clinical presentations for accurate test results. It should also be collected promptly and in a way that minimizes contamination.
The sample collection process must also not put the laboratory staff at risk of infection. That’s why the correct collection and protective equipment must be used in the process. The sample should be labeled appropriately using the correct forms and stored or transported correctly.
Precautions in Specimen Collection
Any fluid or tissue collected as a specimen carries the risk of splash or inoculation injury. As such, standard prevention and control measures must be followed. They include
- Hand hygiene principles;
- Hospital environmental hygiene principles;
- Proper handling of sharps in use and disposal;
- Personal protective equipment or wear;
- Principles of asepsis.
The equipment required in each procedure depends on the specimen to be collected. Using the wrong specimen container can affect the accuracy of the results. For example, bacteria swabs are transported in a medium that’s not compatible with viruses.
The equipment to use includes a polythene transportation bag, disposable gloves and apron, a protective tray, and a sterile specimen container. Other requirements are a laboratory specimen form and a biohazard label.
Request Forms
The laboratory test request forms are an essential part of the sample collection process. Information captured on the form includes the patient’s name, age, department, and patient identification number.
It also must show:
- The type of specimen collection and from where
- Investigations require
- Date and time of specimen collection
- Diagnosis, history, and the reason for the request
- The rationale used in taking the sample
- History of any antimicrobial drugs administered to the patient if possible
- Contact information of the health professional who ordered the investigation
- The form must also have a high-risk label if required.
Transporting Specimens
It’s a requirement that all specimen containers must be carried in a self-sealing polythene bag. It should have two compartments where the container and request form are placed separately.
Specimens should be received in the lab as fast as possible after collection. This reduces the chances of altering their quality or exposing them to contamination and hence affecting the results. Where immediate transportation is not possible, guidelines on the storage of specimens should be followed.
Avoiding Common Problems in Specimen Collection
Most of the problems associated with specimen collection can be prevented with careful attention to routine procedures. The materials provided by the laboratory should be maintained at high quality and used in strict accordance with the guidelines. The volume required for each sample is indicated in the directory referred to previously.
Healthcare providers must also remember to check that the collection materials are not expired. The specimen must be labeled correctly and ensure the sample quantity is sufficient. The container lids must be carefully tightened to avoid leakage or potential contamination. Maintain the specimen at the indicated temperature levels.
Final Thoughts
There are many details, procedures, and analyses related to specimen collection, handling, and storage. It’s essential to be informed, especially as a health practitioner or healthcare provider. It also helps to have this general knowledge as a patient. Regardless of the end of the spectrum that you fall, there’s a lot to learn. Consider enrolling in specimen collection courses that teach more about the principles and procedures if this is your interest area.